Abstract
BACKGROUND About one-third of Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) arises primarily from extranodal sites, patients with extranodal involvement indicate poor clinical outcomes. It is an urgent need to find new treatments for DLBCL patients with extranodal involvement.
METHODS We conducted a single-arm, prospective phase II trial for newly diagnosed DLBCL with extranodal involvement to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Zanubrutinib combined with R-CHOP Regimen.Patients received therapies: R-CHOP(intravenously Rituximab (375mg/m2 on Day0), Cyclophosphamide (750mg/m2 on Day1),Doxorubicin (50mg/m2 on Day1), Vincristine(1.4mg/m2 on Day 1), and oral Prednisone(50mg QD Day1-5) with Zanubrutinib (160mg BID Day 1-21) regimen.
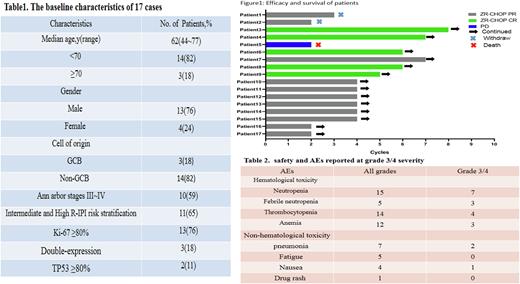
RESULTS 17 patients received ZR-CHOP regimen treatments at least 2 cycles, median treatments cycles were 4 cycles. The median age of the patients is 62 year (49-77y).11 patients (65%) were classified as medium and high-risk group according to IPI or aaIPI Prognostic Scoring. 10 patients (59%) had stage III~IV disease, 14 patients (82%) were Non-GCB types, 13 patients (76%) with Ki-67 more than 80% in pathological IHC. 3 patients (18%) were diagnosed as double-expression lymphoma and 2 patients (11%) with p53 positive over 80% in pathological IHC(Table1). At data cut off , the objective response rate(ORR) of 17 patients was 94%(16/17), 5 patients(30%) reached complete remission(CR) , 2 patients (11%) withdrew from the clinical trial for intolerable adverse reactions and 1 patient(6%) died due to progression disease(PD)(Figure1). The most common hematological toxicity events were neutrophil count decreased, thrombocytopenia and anemia, with 3-4 level occurrence rate was 41.2%, 23.5% and 17.6%. The most common non-hematological toxicity events were pneumonia,fatigue and nausea.1 patient had rash after medication and no atrial firilation, tumor lysis syndrome or massive hemorrhage were reported(Table2).
CONCLUSIONS Our results showed that Zanubrutinib plus R-CHOP(ZR-CHOP) is a safe and effective regimen for DLBCL patients with extranodal involvement. It indicate that the addition of zanubrutinib to the standard first-line treatment can enable these patients to achieve efficient remission in the early stage and without significantly increasing toxicity.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal